Data
Abstract
Face alignment algorithms locate a set of landmark points in images of faces taken in unrestricted situations. State-of-the-art approaches typically fail or lose accuracy in the presence of occlusions, strong deformations, large pose variations and ambiguous configurations. In this paper we present 3DDE, a robust and efficient face alignment algorithm based on a coarse-to-fine cascade of ensembles of regression trees. It is initialized by robustly fitting a 3D face model to the probability maps produced by a convolutional neural network. With this initialization we address self-occlusions and large face rotations. Further, the regressor implicitly imposes a prior face shape on the solution, addressing occlusions and ambiguous face configurations. Its coarse-to-fine structure tackles the combinatorial explosion of parts deformation. In the experiments performed, 3DDE improves the state-of-the-art in 300W, COFW, AFLW and WFLW data sets. Finally, we perform cross-dataset experiments that reveal the existence of a significant data set bias in these benchmarks.
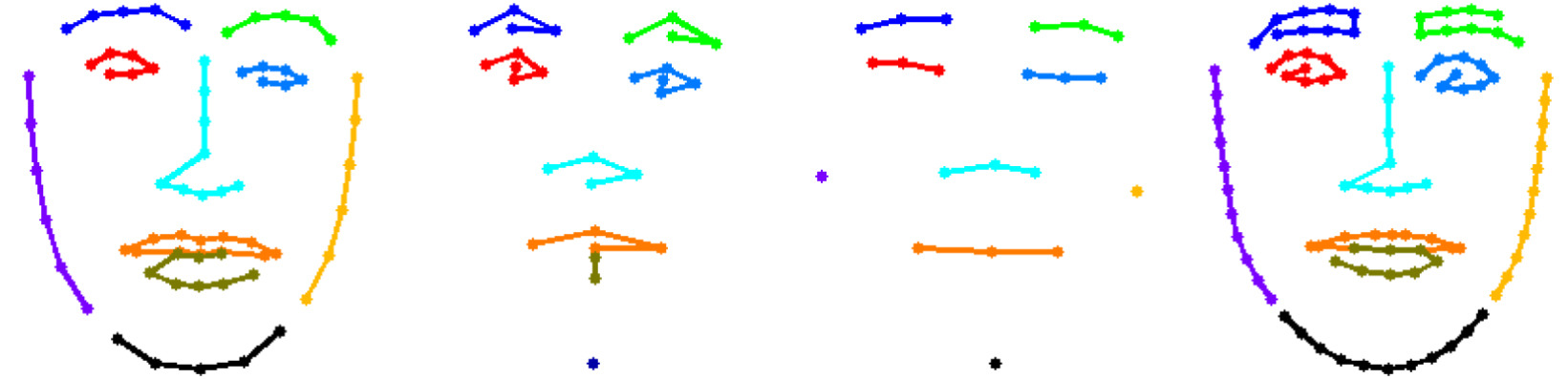
Figure 3: The face parts of 300W, COFW, AFLW and WFLW data bases in the fine stage of our coarse-to-fine ERT
Citation
Roberto Valle and José Miguel Buenaposada and Antonio Valdés and Luis Baumela. Face alignment using a 3D deeply-initialized ensemble of regression trees. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 189 (2019)
@article{Valle19,
author = {Roberto Valle and Jos{\'{e}} Miguel Buenaposada and Antonio Vald{\'{e}}s and Luis Baumela},
title = {Face alignment using a 3D deeply-initialized ensemble of regression trees},
journal = {Comput. Vis. Image Underst.},
volume = {189},
year = {2019},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cviu.2019.102846}
}