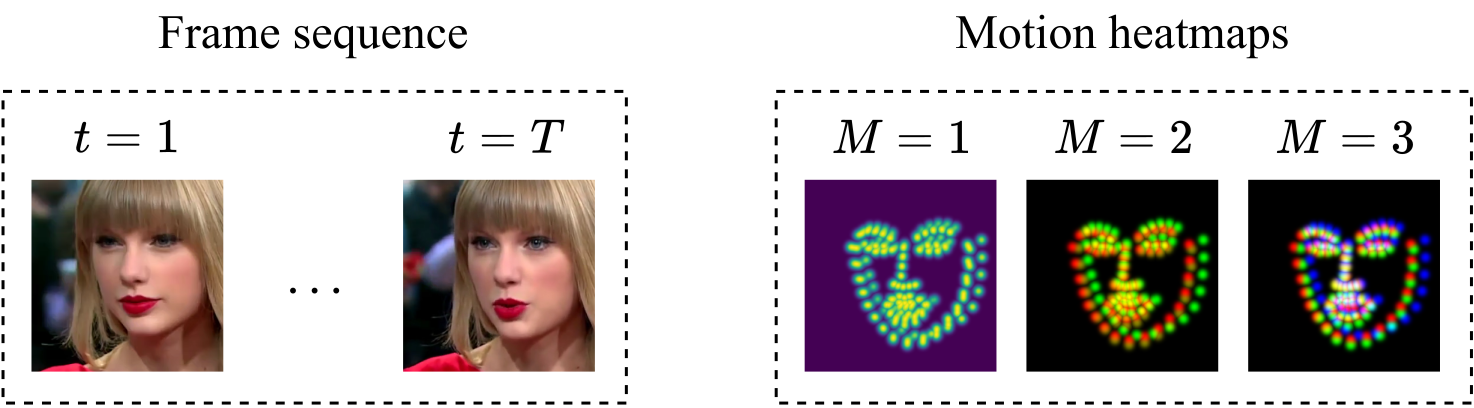
Spatiotemporal Face Alignment for Generalizable Deepfake Detection
In this paper we propose a multi-task network which leverages spatiotemporal features extracted from video inputs to provide more robust predictions compared to image-only models.

In this paper we propose a multi-task network which leverages spatiotemporal features extracted from video inputs to provide more robust predictions compared to image-only models.
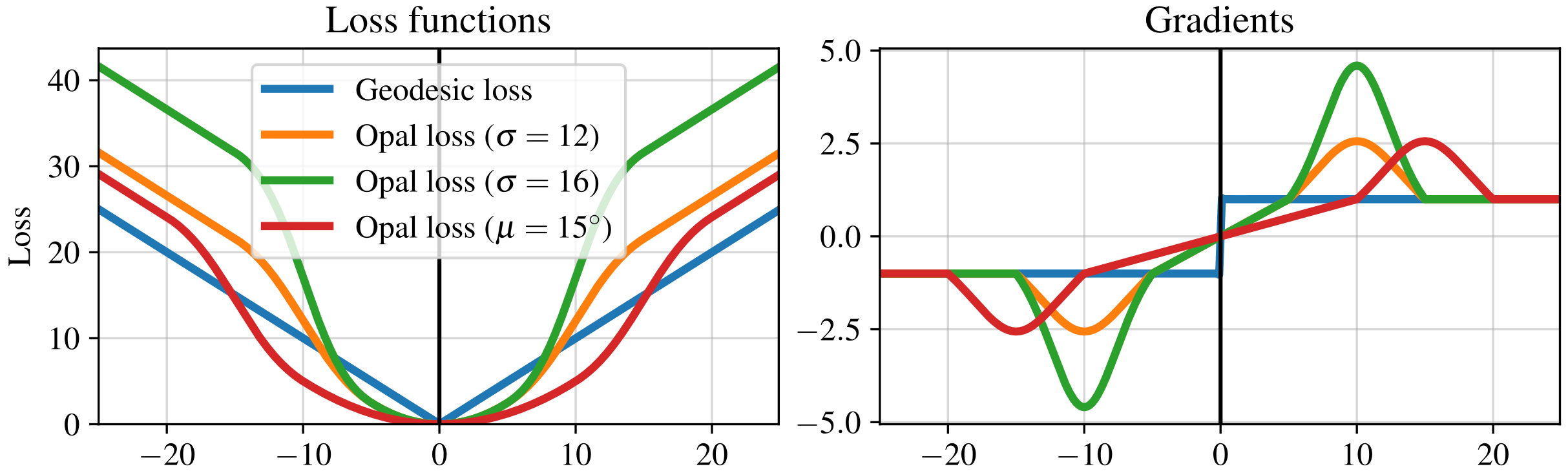
In this paper we analyze the methodology for short- and wide-range HPE and discuss which representations and metrics are adequate for each case.
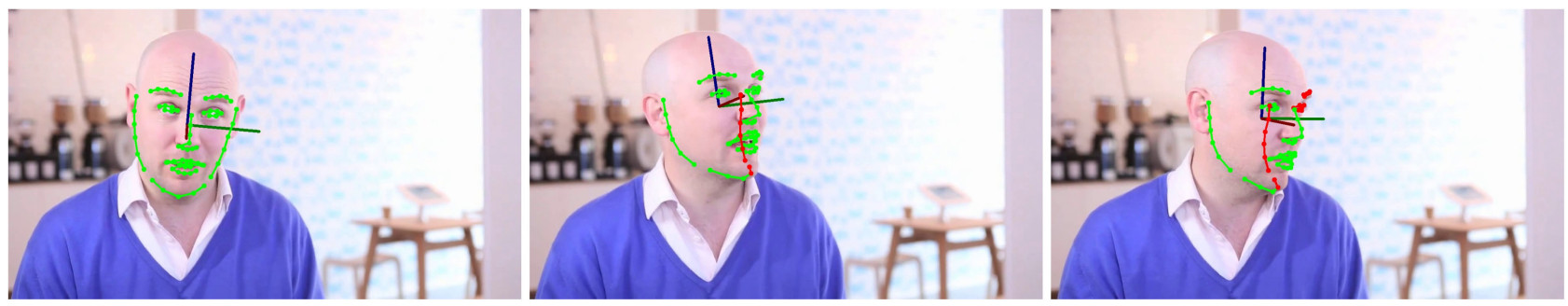
We show that the combination of head pose estimation and landmark-based face alignment significantly improve the performance of the former task.
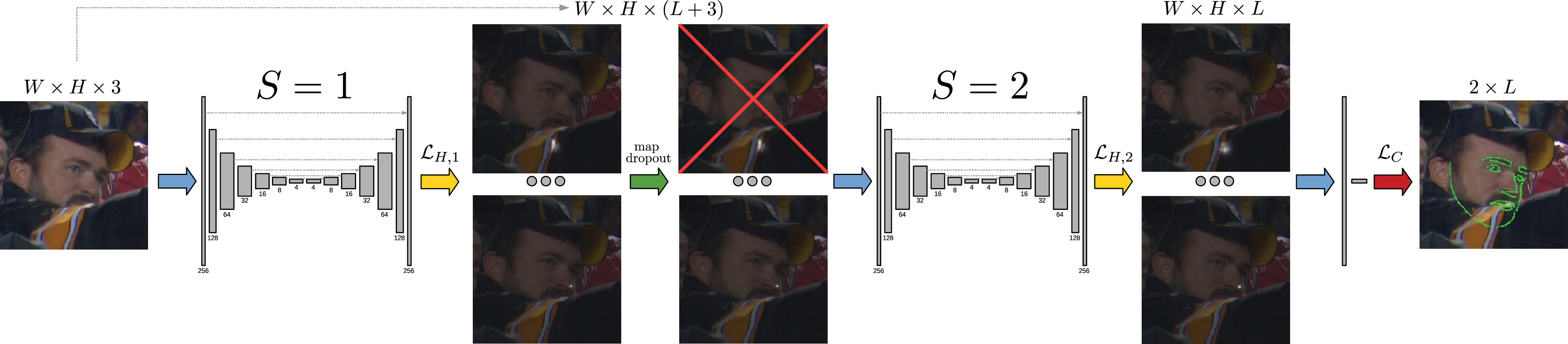
In this paper we investigate the use of a cascade of Neural Net regressors to increase the accuracy of the estimated facial landmarks.
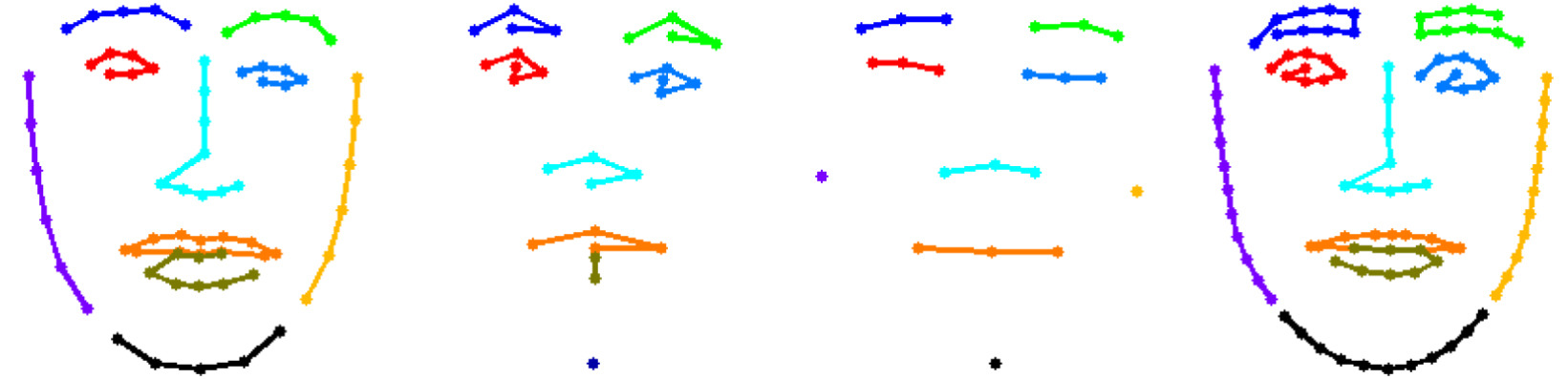
In this paper we present a robust and efficient face alignment algorithm based on a coarse-to-fine cascade of ensembles of regression trees.

In this paper we investigate the use of a cascade of CNN regressors to make the set of estimated landmarks lie closer to a valid face shape.
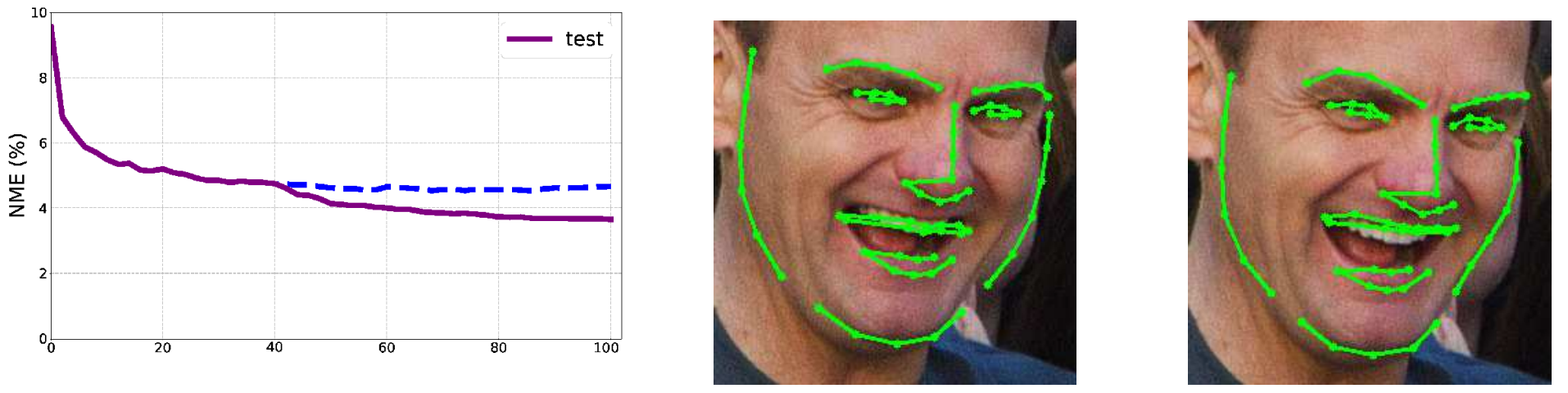
In this paper we present a real-time facial landmark regression method based on a coarse-to-fine Ensemble of Regression Trees (ERT).
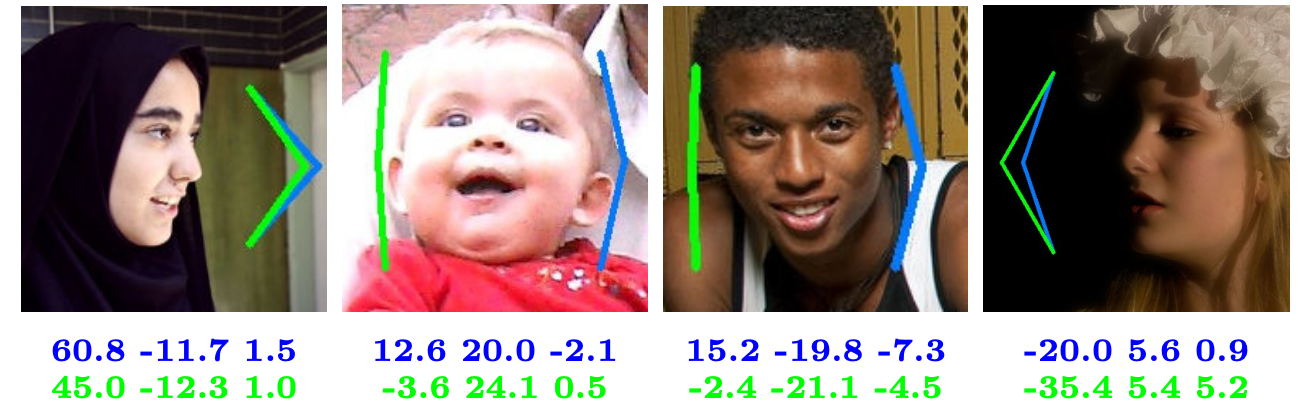

In this paper we present a real-time facial landmark regression method based on a coarse-to-fine Ensemble of Regression Trees (ERT).
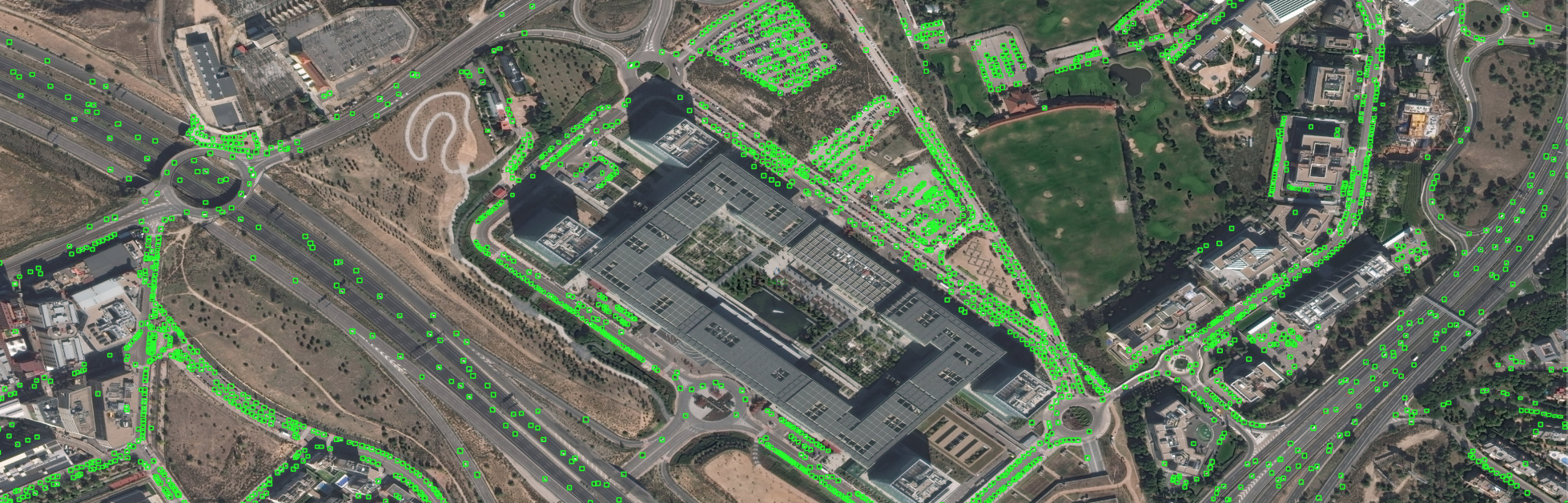
An AI application to estimate the impact of COVID-19 in Madrid.
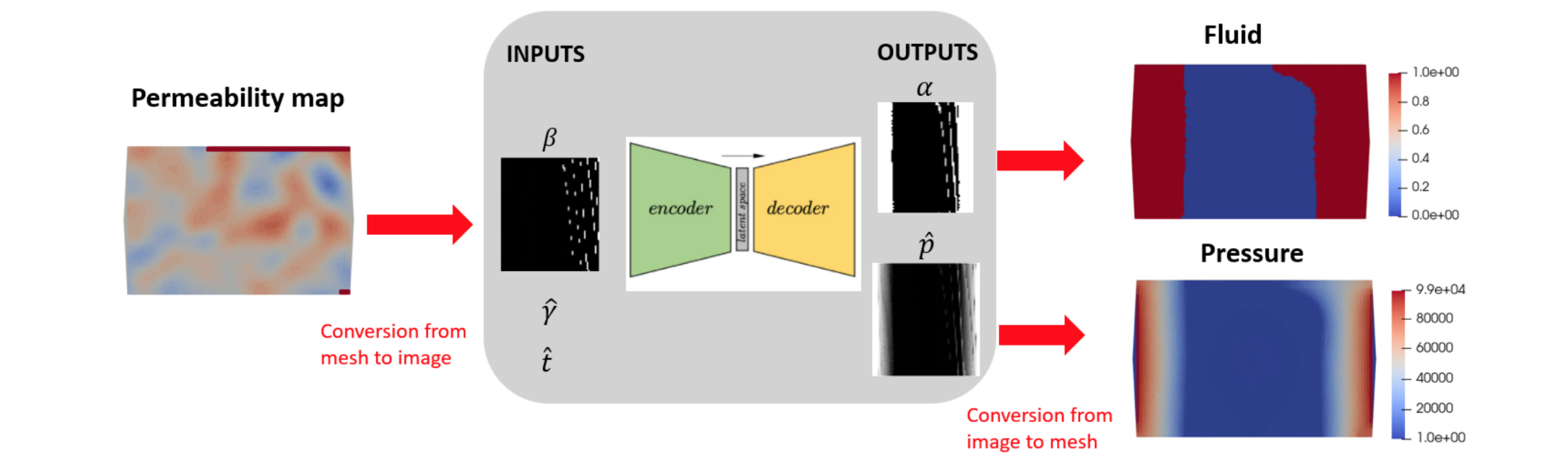
The development of a surrogate model based on a densely connected deep encoder-decoder is employed to overcome current surrogate models limitations.